As a CNC milling student, you’re about to work with one of the most important materials in modern medicine – medical grade titanium. This sleek, silver metal sitting in your workshop will soon become components that help people walk, smile, and live better lives. Let’s explore how your classroom theory transforms into real-world medical miracles.
Why Medical Grade Titanium Matters
Medical grade titanium isn’t just any metal. These specially manufactured round bars meet strict biocompatibility standards, meaning they can safely live inside the human body for decades. The most common grades you’ll work with are:
- Grade 2 Commercially Pure Titanium: Used for dental implants and simple components
- Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5): The workhorse for orthopedic implants like hip and knee replacements
- Grade 23 (Ti-6Al-4V ELI): Extra low interstitial grade for the most demanding applications
Each bar comes with certificates proving its purity, strength, and safety – qualities that make the difference between a successful surgery and a failed implant.
Design Considerations: More Than Just Machining
Before you start your CNC program, remember that medical components require special design thinking:
Surface Finish: Implants need mirror-like surfaces to prevent bacterial growth and ensure smooth integration with body tissues. Your roughness measurements matter more than ever.
Dimensional Accuracy: Tolerance zones that seem tight in regular machining become life-or-death specifications. A hip stem that’s 0.1mm oversized could crack a patient’s femur.
Biocompatibility Features: Many implants include porous surfaces or special coatings to encourage bone growth. Your machining must preserve these critical areas.
Fabrication Methods: Your CNC Skills in Action
Traditional CNC Machining
Most medical components start with subtractive manufacturing. You’ll use:
- Multi-axis milling for complex geometries like hip stems
- Swiss-type lathes for precise dental implant threads
- EDM finishing for ultra-smooth surfaces
Advanced Techniques
Modern medical manufacturing combines multiple approaches:
- Additive manufacturing creates complex internal structures
- Hybrid machining combines 3D printing with traditional CNC finishing
- Micro-machining produces tiny components for delicate surgeries
Real-World Applications: Where Your Work Goes
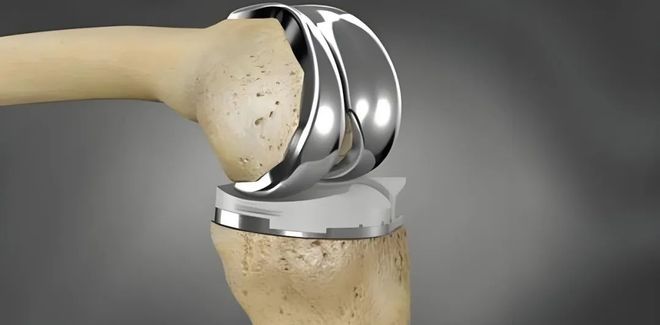
Orthopedic Implants
The hip replacement components you machine will help patients walk pain-free for 20+ years. Knee implants restore mobility to millions. Spinal rods straighten curved backs and relieve chronic pain.
Dental Applications
Dental implants are perhaps the most common titanium components you’ll produce. These threaded posts replace tooth roots, supporting crowns that look and feel like natural teeth. The precision threading you learn is crucial – too loose and the implant fails, too tight and the bone cracks.
Specialized Components
- Cranial plates repair skull fractures
- Cardiovascular stents keep arteries open
- Surgical instruments that never corrode or dull
Manufacturing Considerations for Students
Cutting Parameters
Titanium machines differently than steel or aluminum:
- Lower speeds prevent work hardening
- Consistent feed rates avoid built-up edge
- Flood coolant essential for heat management
- Sharp tools mandatory – dull cutters create problems fast
Quality Control
Every medical component requires documentation:
- Material certificates
- Dimensional inspection reports
- Surface finish measurements
- Traceability through every manufacturing step
Cleanliness Standards
Medical manufacturing demands surgical-level cleanliness. Clean your machine, tools, and workspace like lives depend on it – because they do.
From Student Project to Patient Care
Your practice pieces today prepare you for tomorrow’s responsibilities. Every dimension you check, every surface finish you measure, every program you optimize builds skills that will directly impact patient outcomes.
The titanium round bar on your machine table represents hope for someone facing surgery. Your precision and care transform that raw material into a component that will restore mobility, eliminate pain, or save a life.
Looking for the versatile implant ready to use medical titanium bars, visit this reference page more about the medical-grade titanium bars for your advanced projects and future career applications.
Your Next Steps
Master the fundamentals now:
- Practice dimensional accuracy on every project
- Understand material properties deeply
- Learn quality documentation procedures
- Develop clean manufacturing habits
The medical device industry needs skilled CNC machinists who understand both the technical requirements and the human impact of their work. Your education in titanium machining opens doors to a career where engineering precision meets human compassion – making you part of the team that gives people their lives back, one perfectly machined component at a time.