Mastering the Apex Locator: Your Essential Guide to Accurate Root Canal Length Determination
Welcome, dental students! Accurate determination of root canal length is paramount for successful endodontic treatment. Over-instrumentation or under-instrumentation can lead to complications and treatment failure. The apex locator is an indispensable tool that significantly enhances the precision of this crucial step. This tutorial will guide you through the essentials of using an apex locator effectively.
What is an Apex Locator?
An apex locator is an electronic device used in endodontics to determine the working length of a root canal. It relies on measuring the electrical resistance or impedance between an electrode attached to an endodontic file inside the tooth and another electrode placed on the patient’s lip or oral mucosa.
The Science Behind the Measurement:
Most modern apex locators utilize the principle of impedance or frequency-dependent impedance. Different tissues within and around the tooth exhibit varying electrical properties. The enamel and dentin are highly resistive, while the periodontal ligament (PDL) has a significantly lower resistance. The apex locator detects the characteristic change in impedance as the file tip reaches the apical constriction (the narrowest part of the root canal, ideally where instrumentation should end) or the apical foramen (the actual exit of the root canal).
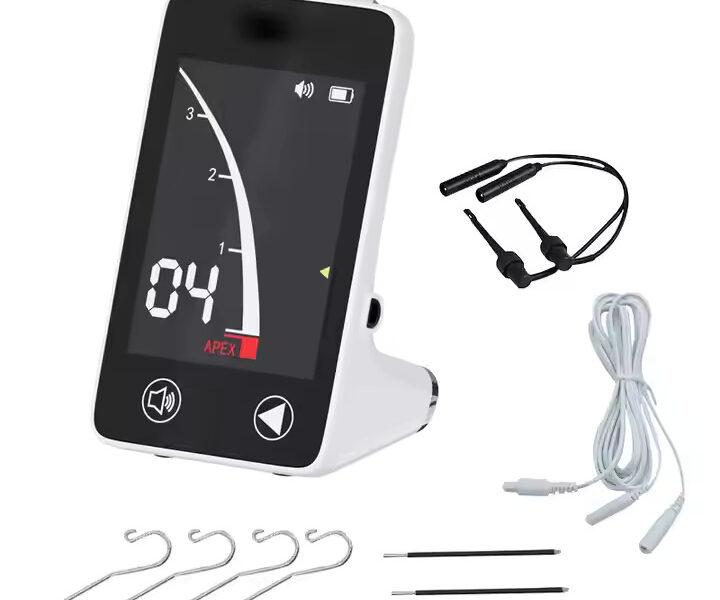
Components of a Typical Apex Locator:
- Main Unit: Houses the electronic circuitry and displays the readings.
- File Clip: Attaches to the endodontic file.
- Lip Hook (or Counter Electrode): Contacts the patient’s lip or oral mucosa.
- Connecting Wires: Connect the file clip and lip hook to the main unit.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using an Apex Locator:
- Gain Access: Ensure proper access cavity preparation and locate the canal orifice(s). Remove any pulp tissue and debris from the pulp chamber.
- Select the Correct File: Choose an appropriately sized manual endodontic file (usually a size 10 or 15 K-file) that can passively reach the apical third of the canal. For curved or narrow canals, using a smaller file initially is recommended. Do not use rotary files for initial length determination with an apex locator.
- Attach the File Clip: Securely attach the file clip to the selected endodontic file. Ensure good contact.
- Attach the Lip Hook: Place the lip hook on the patient’s lip or oral mucosa, ensuring good contact. The area should be dry for optimal conductivity.
- Turn on the Apex Locator: Switch on the apex locator. Some units may require calibration or a zeroing step before use – refer to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Introduce the File: Gently insert the file into the canal orifice. Advance the file slowly and carefully towards the apex.
- Monitor the Reading: Observe the display of the apex locator. The readings will change as the file progresses through the canal. Different apex locators have varying displays (e.g., bar graphs, numerical readings, color-coded zones). Familiarize yourself with the specific indications of your unit.
- Reach the Apical Constriction: Continue advancing the file until the apex locator indicates that the file tip has reached the apical constriction or the desired endpoint. This is often indicated by a specific visual or auditory signal (e.g., a steady tone, a specific icon appearing on the screen, or a numerical reading indicating the “APEX”).
- Confirm and Record the Length: Once the apex is indicated, gently move the file slightly coronally and apically to confirm the reading. Note the length displayed on the apex locator. This is your electronic working length.
- Adjust for Working Length: The electronic apex length often corresponds to the apical constriction. For instrumentation purposes, the working length is typically established 0.5-1.0 mm short of the apex to avoid over-instrumentation. Subtract this distance from the electronically measured length to determine your final working length.
- Verify (Optional but Recommended): If possible, and as per your clinical training, consider verifying the working length with a periapical radiograph, especially in complex cases.
Essential Tips for Accurate Apex Locator Usage:
- Remove Pulp Tissue and Debris: Thoroughly clean the pulp chamber and irrigate the canal to remove debris, which can affect the accuracy of the apex locator.
- Use a Lubricant: Employ a suitable endodontic lubricant to facilitate file movement and improve the consistency of readings.
- Avoid Short Circuits: Ensure the file clip and lip hook are not in contact with each other or any metallic restorations, as this can cause inaccurate readings.
- Follow Manufacturer Instructions: Each apex locator model may have specific operating instructions. Always refer to the manufacturer’s manual for detailed guidance.
- Consider Canal Morphology: In cases of complex canal anatomy (e.g., apical deltas, lateral canals), the apex locator provides a valuable guide, but clinical judgment and radiographic assessment remain crucial.
- Practice Makes Perfect: Like any clinical skill, proficiency in using an apex locator comes with practice. Utilize training models and seek guidance from your instructors.
For dental professional, and dental students who are interested in the apex locator with endo motor, we invite you to explore this link for expex locator through Dental Lab Shop.
Advantages of Using an Apex Locator:
- Increased Accuracy: Provides a more objective and precise method for determining root canal length compared to relying solely on radiographs.
- Reduced Radiation Exposure: Minimizes the need for multiple radiographs to determine working length.
- Time Efficiency: Can often determine root canal length more quickly than traditional radiographic methods.
- Improved Patient Comfort: Reduces the number of radiographs needed, enhancing patient comfort.
Mastering the use of the apex locator is a fundamental skill in modern endodontics. By understanding its principles, following the correct procedures, and adhering to best practices, you will significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of your root canal treatments, ultimately leading to better outcomes for your patients. Keep practicing, and don’t hesitate to ask your instructors for guidance! Sources and related content